
Technical Analysis from A to Z
by Steven B. Achelis
TRENDLINES
Overview
One of the basic tenets put forth by Charles Dow in the Dow Theory is that security prices do trend. Trends are often measured and identified by "trendlines." A trendline is a sloping line that is drawn between two or more prominent points on a chart. Rising trends are defined by a trendline that is drawn between two or more troughs (low points) to identify price support. Falling trend-s are defined by trendlines that are drawn between two or more peaks (high points) to identify price resistance.
Interpretation
A principle of technical analysis is that once a trend has been formed (two or more peaks/troughs have touched the trendline and reversed direction) it will remain intact until broken.
That sounds much more simplistic than it is! The goal is to analyze the current trend using trendlines and then either invest with the current trend until the trendline is broken, or wait for the trendline to be broken and then invest with the new (opposite) trend.
One benefit of trendlines is they help distinguish emotional decisions ("I think it's time to sell...") from analytical decisions ("I will hold until the current rising trendline is broken"). Another benefit of trendlines is that they almost always keep you on the "right" side of the market. When using trendlines, it's difficult to hold a security for very long when prices are falling just as it's hard to be short when prices are rising--either way the trendline will be broken.
Example
The following chart shows Goodyear along with several trendlines.
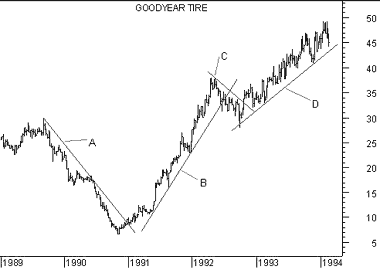
Trendlines "A" and "C" are falling trendlines. Note how they were drawn between successive peaks. Trendlines "B" and "D" are rising trendlines. They were drawn between successive troughs in the price.
Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Terminology
- To Learn More
- Bibliography
- About the Author
- Technical Analysis
- Price Fields
- Charts
- Support & Resistance
- Trends
- Moving Averages
- Indicators
- Market Indicators
- Line Studies
- Periodicity
- The Time Element
- Conclusion
- Absolute Breadth Index
- Accumulation/Distribution
- Accumulation Swing Index
- Advance/Decline Line
- Advance/Decline Ratio
- Advancing-Declining Issues
- Advancing, Declining, Unchanged Volume
- Andrews' Pitchfork
- Arms Index
- Average True Range
- Bollinger Bands
- Breadth Thrust
- Bull/Bear Ratio
- Candlesticks - Japanese
- CANSLIM
- Chaikin Oscillator
- Commodity Channel Index
- Commodity Selection Index
- Correlation Analysis
- Cumulative Volume Index
- Cycles
- Demand Index
- Detrended Price Oscillator
- Directional Movement
- Dow Theory
- Ease of Movement
- Efficient Market Theory
- Elliott Wave Theory
- Envelopes (Trading Bands)
- Equivolume/Candlevolume
- Fibonacci Studies
- Four Percent Model
- Fourier Transform
- Fundamental Analysis
- Gann Angles
- Herrick Payoff Index
- Interest Rates
- Kagi
- Large Block Ratio
- Linear Regression Lines
- MACD
- Mass Index
- McClellan Oscillator
- McClellan Summation Index
- Median Price
- Member Short Ratio
- Momentum
- Money Flow Index
- Moving Averages
- Negative Volume Index
- New Highs-Lows Cumulative
- New Highs-New Lows
- New Highs/Lows Ratio
- Odd Lot Balance Index
- Odd Lot Purchases/Sales
- Odd Lot Short Ratio
- On Balance Volume
- Open Interest
- Open-10 TRIN
- Option Analysis
- Overbought/Oversold
- Parabolic SAR
- Patterns
- Percent Retracement
- Performance
- Point & Figure
- Positive Volume Index
- Price and Volume Trend
- Price Oscillator
- Price Rate-of-Change
- Public Short Ratio
- Puts/Calls Ratio
- Quadrant Lines
- Relative Strength, Comparative
- Relative Strength Index
- Renko
- Speed Resistance Lines
- Spreads
- Standard Deviation
- STIX
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Swing Index
- Three Line Break
- Time Series Forcast
- Tirone Levels
- Total Short Ratio
- Trade Volume Index
- Trendlines
- TRIX
- Typical Price
- Ultimate Oscillator
- Upside/Downside Ratio
- Upside/Downside Volume
- Vertical Horizonal Filter
- Volatility, Chaikin's
- Volume
- Volume Oscillator
- Volume Rate-of-Change
- Weighted Close
- Williams' Accumulation/Distribution
- Williams' %R
- Zig Zag