
Technical Analysis from A to Z
by Steven B. Achelis
ON BALANCE VOLUME
Overview
On Balance Volume ("OBV") is a momentum indicator that relates volume to price change.
On Balance Volume was developed by Joe Granville and originally presented in his book New Strategy of Daily Stock Market Timing for Maximum Profits.
Interpretation
On Balance Volume is a running total of volume. It shows if volume is flowing into or out of a security. When the security closes higher than the previous close, all of the day's volume is considered up-volume. When the security closes lower than the previous close, all of the day's volume is considered down-volume.
A full explanation of OBV is beyond the scope of this book. If you would like further information on OBV analysis, I recommend that you read Granville's book, New Strategy of Daily Stock Market Timing for Maximum Profits.
The basic assumption, regarding OBV analysis, is that OBV changes precede price changes. The theory is that smart money can be seen flowing into the security by a rising OBV. When the public then moves into the security, both the security and the OBV will surge ahead.
If the security's price movement precedes OBV movement, a "non-confirmation" has occurred. Non-confirma-tions can occur at bull market tops (when the security rises without, or before, the OBV) or at bear market bottoms (when the security falls without, or before, the OBV).
The OBV is in a rising trend when each new peak is higher than the previous peak and each new trough is higher than the previous trough. Likewise, the OBV is in a falling trend when each successive peak is lower than the previous peak and each successive trough is lower than the previous trough. When the OBV is moving sideways and is not making successive highs and lows, it is in a doubtful trend. [See Figure 47]
Figure 47
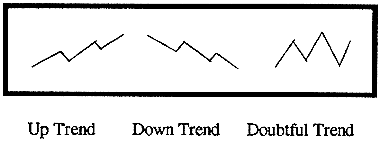
Once a trend is established, it remains in force until it is broken. There are two ways in which the OBV trend can be broken. The first occurs when the trend changes from a rising trend to a falling trend, or from a falling trend to a rising trend.
The second way the OBV trend can be broken is if the trend changes to a doubtful trend and remains doubtful for more than three days. Thus, if the security changes from a rising trend to a doubtful trend and remains doubtful for only two days before changing back to a rising trend, the OBV is consid-ered to have always been in a rising trend.
When the OBV changes to a rising or falling trend, a "breakout" has occurred. Since OBV breakouts normally precede price breakouts, investors should buy long on OBV upside breakouts. Likewise, investors should sell short when the OBV makes a downside breakout. Positions should be held until the trend changes (as explain-ed in the preceding paragraph).
This method of analyzing On Balance Volume is designed for trading short-term cycles. According to Granville, investors must act quickly and decisively if they wish to profit from short-term OBV analysis.
Example
The following chart shows Pepsi and the On Balance Volume indicator. I have labeled the OBV Up, Down, and Doubtful trends.
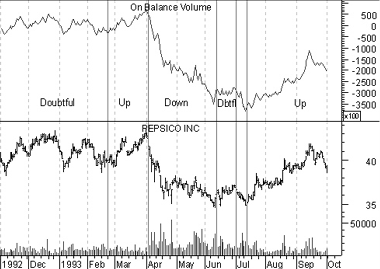
A falling trend, as you will recall, is defined by lower peaks and lower troughs. Conversely, a rising trend is defined by higher peaks and higher troughs.
Calculation
On Balance Volume is calculated by adding the day's volume to a cumulative total when the security's price closes up, and subtracting the day's volume when the security's price closes down.
If today's close is greater than yesterday's close then:
![]()
If today's close is less than yesterday's close then:
![]()
If today's close is equal to yesterday's close then:
![]()
Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Terminology
- To Learn More
- Bibliography
- About the Author
- Technical Analysis
- Price Fields
- Charts
- Support & Resistance
- Trends
- Moving Averages
- Indicators
- Market Indicators
- Line Studies
- Periodicity
- The Time Element
- Conclusion
- Absolute Breadth Index
- Accumulation/Distribution
- Accumulation Swing Index
- Advance/Decline Line
- Advance/Decline Ratio
- Advancing-Declining Issues
- Advancing, Declining, Unchanged Volume
- Andrews' Pitchfork
- Arms Index
- Average True Range
- Bollinger Bands
- Breadth Thrust
- Bull/Bear Ratio
- Candlesticks - Japanese
- CANSLIM
- Chaikin Oscillator
- Commodity Channel Index
- Commodity Selection Index
- Correlation Analysis
- Cumulative Volume Index
- Cycles
- Demand Index
- Detrended Price Oscillator
- Directional Movement
- Dow Theory
- Ease of Movement
- Efficient Market Theory
- Elliott Wave Theory
- Envelopes (Trading Bands)
- Equivolume/Candlevolume
- Fibonacci Studies
- Four Percent Model
- Fourier Transform
- Fundamental Analysis
- Gann Angles
- Herrick Payoff Index
- Interest Rates
- Kagi
- Large Block Ratio
- Linear Regression Lines
- MACD
- Mass Index
- McClellan Oscillator
- McClellan Summation Index
- Median Price
- Member Short Ratio
- Momentum
- Money Flow Index
- Moving Averages
- Negative Volume Index
- New Highs-Lows Cumulative
- New Highs-New Lows
- New Highs/Lows Ratio
- Odd Lot Balance Index
- Odd Lot Purchases/Sales
- Odd Lot Short Ratio
- On Balance Volume
- Open Interest
- Open-10 TRIN
- Option Analysis
- Overbought/Oversold
- Parabolic SAR
- Patterns
- Percent Retracement
- Performance
- Point & Figure
- Positive Volume Index
- Price and Volume Trend
- Price Oscillator
- Price Rate-of-Change
- Public Short Ratio
- Puts/Calls Ratio
- Quadrant Lines
- Relative Strength, Comparative
- Relative Strength Index
- Renko
- Speed Resistance Lines
- Spreads
- Standard Deviation
- STIX
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Swing Index
- Three Line Break
- Time Series Forcast
- Tirone Levels
- Total Short Ratio
- Trade Volume Index
- Trendlines
- TRIX
- Typical Price
- Ultimate Oscillator
- Upside/Downside Ratio
- Upside/Downside Volume
- Vertical Horizonal Filter
- Volatility, Chaikin's
- Volume
- Volume Oscillator
- Volume Rate-of-Change
- Weighted Close
- Williams' Accumulation/Distribution
- Williams' %R
- Zig Zag