
Technical Analysis from A to Z
by Steven B. Achelis
VERTICAL HORIZONTAL FILTER
Overview
The Vertical Horizontal Filter ("VHF") determines whether prices are in a trending phase or a congestion phase.
The VHF was first presented by Adam White in an article published in the August, 1991 issue of Futures Magazine.
Interpretation
Probably the biggest dilemma in technical analysis is determining if prices are trending or are in a trading-range. Trend-following indicators such as the MACD and moving averages are excellent in trending markets, but they usually generate multiple conflicting trades during trading-range (or "congestion") periods. On the other hand, oscillators such as the RSI and Stochastics work well when prices fluctuate within a trading range, but they almost always close positions prematurely during trending markets. The VHF indicator attempts to determine the "trendiness" of prices to help you decide which indicators to use.
There are three ways to interpret the VHF indicator:
- You can use the VHF values themselves to determine the degree that prices are trending. The higher the VHF, the higher the degree of trending and the more you should be using trend-following indicators.
- You can use the direction of the VHF to determine whether a trending or congestion phase is developing. A rising VHF indicates a developing trend; a falling VHF indicates that prices may be entering a congestion phase.
- You can use the VHF as a contrarian indicator. Expect congestion periods to follow high VHF values; expect prices to trend following low VHF values.
Example
The following chart shows Motorola and the VHF indicator.
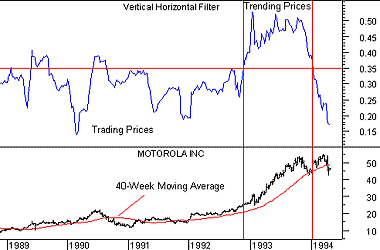
The VHF indicator was relatively low from 1989 through most of 1992. These low values showed that prices were in a trading range. From late-1992 through 1993 the VHF was significantly higher. These higher values indicated that prices were trending.
The 40-week (i.e., 200-day) moving average on Motorola's prices demonstrates the value of the VHF indicator. You can see that a classic moving average trading system (buy when prices rise above their moving average and sell when prices fall below their average) worked well in 1992 and 1993, but generated numerous whipsaws when prices were in a trading range.
Calculation
To calculate the VHF indicator, first determine the highest closing price ("HCP") and the lowest closing price ("LCP") over the specified time period (often 28-days).
![]()
![]()
Next, subtract the lowest closing price from the highest closing price and take the absolute value of this difference. This value will be the numerator.
![]()
To determine the denominator, sum the absolute value of the difference between each day's price and the previous day's price over the specified time periods.
![]()
The VHF is then calculated by dividing the previously defined numerator by the denominator.
![]()
Contents
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- Terminology
- To Learn More
- Bibliography
- About the Author
- Technical Analysis
- Price Fields
- Charts
- Support & Resistance
- Trends
- Moving Averages
- Indicators
- Market Indicators
- Line Studies
- Periodicity
- The Time Element
- Conclusion
- Absolute Breadth Index
- Accumulation/Distribution
- Accumulation Swing Index
- Advance/Decline Line
- Advance/Decline Ratio
- Advancing-Declining Issues
- Advancing, Declining, Unchanged Volume
- Andrews' Pitchfork
- Arms Index
- Average True Range
- Bollinger Bands
- Breadth Thrust
- Bull/Bear Ratio
- Candlesticks - Japanese
- CANSLIM
- Chaikin Oscillator
- Commodity Channel Index
- Commodity Selection Index
- Correlation Analysis
- Cumulative Volume Index
- Cycles
- Demand Index
- Detrended Price Oscillator
- Directional Movement
- Dow Theory
- Ease of Movement
- Efficient Market Theory
- Elliott Wave Theory
- Envelopes (Trading Bands)
- Equivolume/Candlevolume
- Fibonacci Studies
- Four Percent Model
- Fourier Transform
- Fundamental Analysis
- Gann Angles
- Herrick Payoff Index
- Interest Rates
- Kagi
- Large Block Ratio
- Linear Regression Lines
- MACD
- Mass Index
- McClellan Oscillator
- McClellan Summation Index
- Median Price
- Member Short Ratio
- Momentum
- Money Flow Index
- Moving Averages
- Negative Volume Index
- New Highs-Lows Cumulative
- New Highs-New Lows
- New Highs/Lows Ratio
- Odd Lot Balance Index
- Odd Lot Purchases/Sales
- Odd Lot Short Ratio
- On Balance Volume
- Open Interest
- Open-10 TRIN
- Option Analysis
- Overbought/Oversold
- Parabolic SAR
- Patterns
- Percent Retracement
- Performance
- Point & Figure
- Positive Volume Index
- Price and Volume Trend
- Price Oscillator
- Price Rate-of-Change
- Public Short Ratio
- Puts/Calls Ratio
- Quadrant Lines
- Relative Strength, Comparative
- Relative Strength Index
- Renko
- Speed Resistance Lines
- Spreads
- Standard Deviation
- STIX
- Stochastic Oscillator
- Swing Index
- Three Line Break
- Time Series Forcast
- Tirone Levels
- Total Short Ratio
- Trade Volume Index
- Trendlines
- TRIX
- Typical Price
- Ultimate Oscillator
- Upside/Downside Ratio
- Upside/Downside Volume
- Vertical Horizonal Filter
- Volatility, Chaikin's
- Volume
- Volume Oscillator
- Volume Rate-of-Change
- Weighted Close
- Williams' Accumulation/Distribution
- Williams' %R
- Zig Zag